Updates
August 2025: Maine Forest Service is working with small landowners in Aroostook County who may be impacted by growing spruce budworm (SBW) populations to have their woodlots considered for inclusion in next year’s aerial treatment program.
June 2025: The Maine Budworm Response Coalition (MBRC) concluded aerial treatments to reduce spruce budworm (SBW) populations before populations build to an outbreak using an approach called Early Intervention Strategy (EIS). Read more below.
Background
The Maine Budworm Response Coalition (MBRC), comprised of timberland owners and managers in Maine, successfully advocated for emergency funding to oversee and implement the Early Intervention Strategy (EIS) methods to reduce the rising SBW populations and protect the health of our forest ecosystems and resources, maintain wildlife habitat, and prevent impacts to our forest-based economy.
The MBRC collaborated with the Maine Forest Service (MFS), who provided technical assistance and communication with landowners and the public regarding biology, management options, and SBW history. Additionally, the MFS provided financial oversight and reimbursement for the state and federal funds supporting the SBW response. For more information on the funding details, please visit the Maine Forest Service Spruce Budworm website.
The MBRC worked with landowners, scientists, the University of Maine, and other agencies to determine where treatment is needed and how to best target those areas to reduce SBW populations below the outbreak threshold. To achieve this goal, the MBRC coordinated the administration of low-toxicity insecticides through an aerial spray program that completed in early June 2025. Roughly 240,000 acres in northern Maine with larval populations at or exceeding the outbreak threshold were targeted.
Where did the 2025 Aerial Spray Program happen?
The MBRC conducted aerial applications in the Aroostook County towns of: Allagash, Big Twenty Twp., New Canada, St. John Plt., T11 R15, T13 R15, T13 R16, T14 R11, T14 R12, T14 R14, T14 R15, T14 R16, T15 R10, T15 R11, T15 R12, T15 R13, T15 R14, T15 R15, T16 R12, T16 R13, T16 R14, T16 R5, T17 R12, T17 R13, T17 R14, T17 R4, T17 R5, T18 R10 T18 R11, T18 R12, T18 R13, T19 R11, T19 R12, and Wallagrass during the appropriate window of SBW development, bud development, and weather conditions.
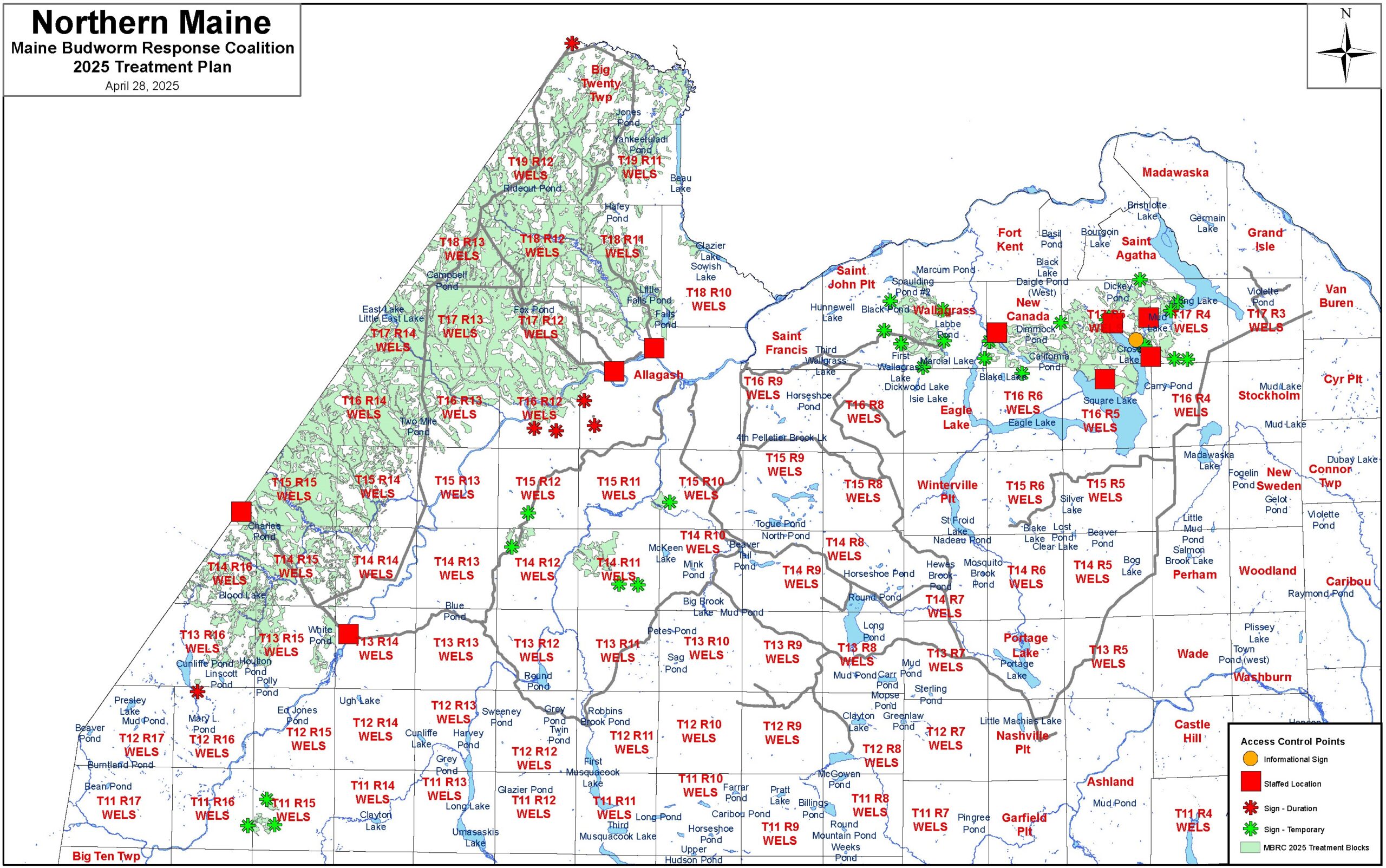
For more information about treatment locations email mainebudwormrc@gmail.com.
What insecticides were used?
Insecticides containing active ingredients tebufenozide (Mimic) or Btk (Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki, Foray) were applied by helicopter and/or fixed wing aircraft using modern technologies to ensure accurate applications. SBW populations may require additional aerial applications over the coming years to ensure the populations do not reach an outbreak level.
Aerial spraying was only applied:
- Inside predetermined areas of spruce-fir forest with SBW populations that are at or above the action threshold
- No closer than 100 ft from lakes, streams, other bodies of water and ¼ mile from identified habitat of state-endangered and threatened butterflies
- In good weather (no rain or high winds) to prevent drift or unintended applications
- Using reduced-risk insecticides that only affect larvae that eat treated foliage
Still have questions about SBW or the EIS response program?
We’re here to help. Multiple organizations are involved in the monitoring, research, and response to spruce budworm. Find contacts on our contact page: